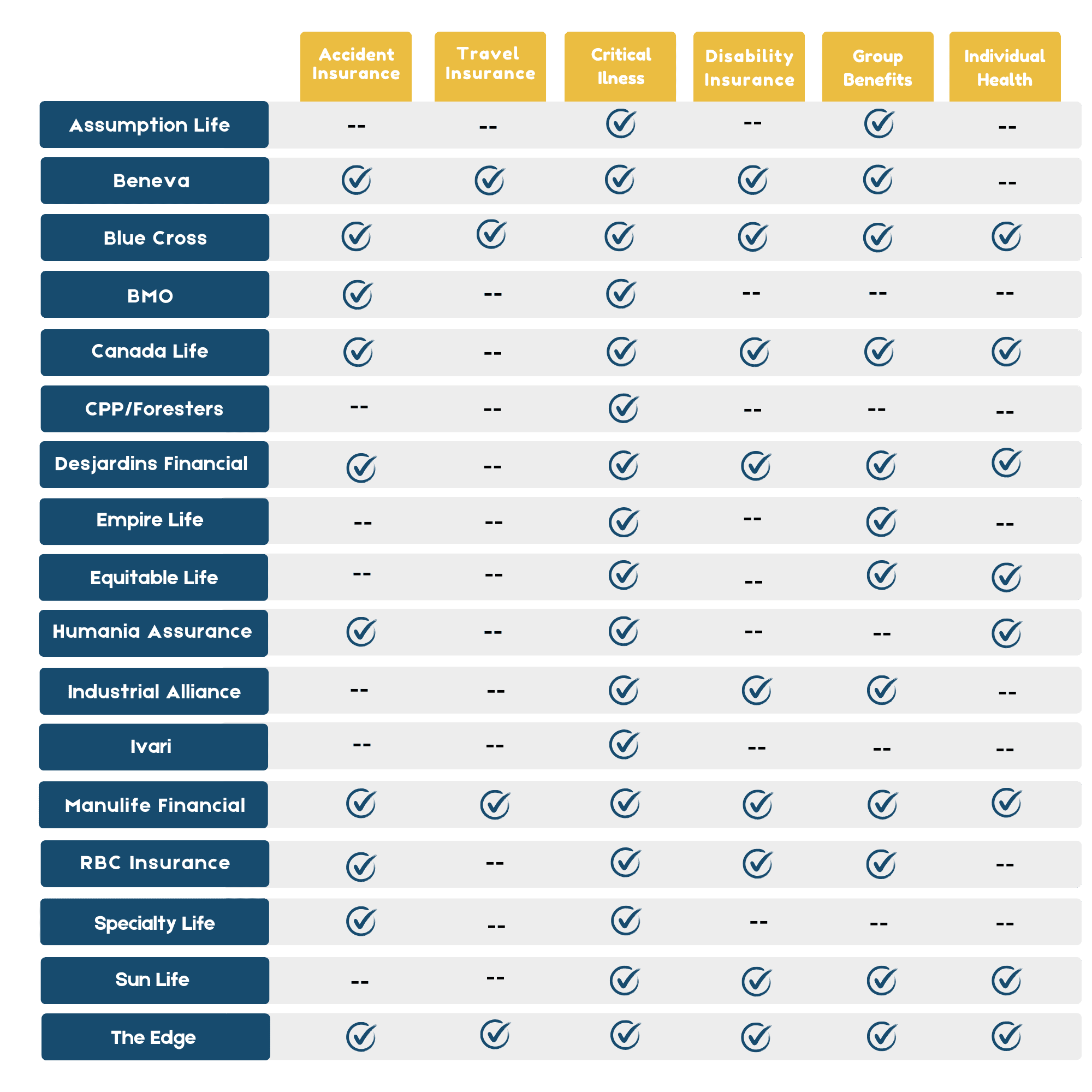
*Les compagnies d'assurance et les produits disponibles au Canada.
Prestations de vie
Qu'est-ce que l'assurance vie ?
L'assurance de prestations en cas de vie, également connue sous le nom de prestations accélérées ou d'avenants, est un type d'assurance qui fournit un soutien financier aux assurés pendant qu'ils sont encore en vie, s'ils souffrent d'une maladie, d'une blessure ou d'un état grave qui affecte de manière significative leur capacité à mener une vie normale. Contrairement à l'assurance vie traditionnelle, qui ne verse un capital décès aux bénéficiaires qu'après le décès de l'assuré, l'assurance vie permet à l'assuré d'accéder à une partie du capital décès de sa police de son vivant, sous certaines conditions.
Ce type d'assurance peut s'avérer crucial pour assurer la stabilité financière et la tranquillité d'esprit des personnes confrontées à des problèmes de santé graves. Il garantit que les assurés disposent des fonds nécessaires pour couvrir une série de dépenses, y compris les factures médicales, les soins de longue durée et les frais de la vie quotidienne, sans avoir à épuiser leur épargne ou à compter uniquement sur d'autres formes d'aide financière.
Avantages
Aide financière : Permet d'accéder immédiatement à des fonds pour les traitements médicaux, l'aménagement du domicile, les soins de longue durée et d'autres dépenses.
Flexibilité : Les fonds peuvent être utilisés à la discrétion de l'assuré, pour payer des factures médicales, des dettes ou des frais de subsistance.
Tranquillité d'esprit : Réduit le stress en garantissant la disponibilité des ressources financières, ce qui permet de se concentrer sur le rétablissement ou de passer du temps de qualité avec ses proches.
Aucun remboursement n'est exigé : Le montant obtenu est déduit du capital décès, sans qu'il soit nécessaire de le rembourser si le preneur d'assurance se rétablit.
Conditions d'éligibilité
L'assurance décès couvre généralement les conditions suivantes :
Maladie grave : Maladies graves telles que le cancer, la crise cardiaque, l'accident vasculaire cérébral ou la défaillance d'un organe majeur. Ces affections nécessitent souvent un traitement lourd et coûteux, qui peut avoir un impact considérable sur les finances d'une personne.
Maladie chronique : Affections de longue durée qui limitent la capacité d'une personne à accomplir les activités de base de la vie quotidienne (AVQ), telles que se laver, s'habiller, s'alimenter et se déplacer. Les exemples incluent l'arthrite sévère, le diabète avec complications et la maladie d'Alzheimer à un stade avancé.
Maladie en phase terminale : Lorsqu'un assuré est atteint d'une maladie en phase terminale et que son espérance de vie est limitée, généralement de 12 à 24 mois. Cela lui permet d'accéder à des fonds pour couvrir les soins de fin de vie, les activités qu'il souhaite faire ou pour alléger la charge financière qui pèse sur ses proches.
FAQ sur les prestations du vivant
Les conditions requises comprennent généralement les maladies graves, chroniques ou terminales telles que le cancer, les maladies cardiaques, les accidents vasculaires cérébraux, la maladie d'Alzheimer et les blessures graves.
Le montant varie selon les polices mais se situe généralement entre 50% et 80% du capital décès.
Non, le montant que vous recevez est déduit du capital décès et vous ne devez pas le rembourser.
Oui, la plupart des polices prévoient un délai d'attente, généralement compris entre 30 et 90 jours après le diagnostic, avant que vous ne puissiez bénéficier des prestations.
Les prestations en cas de vie ne sont généralement pas imposables si le preneur d'assurance a payé les primes avec de l'argent après impôt. Toutefois, il est conseillé de consulter un fiscaliste pour les cas particuliers.
